Abstract
Introduction
Mixed lineage leukemias (MLL) are an extremely aggressive subset of leukemias that are inherently resistant to several therapies. MLL aberrations (deletion KMT2A and MLL rearrangements) are extremely rare in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and little is known regarding their clinical course or outcomes. The aim of the study is to determine the natural course of the disease in our patient population.
Methods
A retrospective cytogenetic database search of patients presenting to a tertiary cancer center from January 2005 to February 2021 with the diagnosis of MDS and CMML with presence of MLL aberrations was conducted. Deletion KMT2A was defined as deletion of 11q23 on cytogenetic studies. Patients who had received prior therapy with hypomethylating agents (HMAs), cytarabine-based regimens, or intensive chemotherapy were excluded. The International Working Group 2006 criteria was used for response assessment. Progression-free survival (PFS) was calculated from date of diagnosis to date of progression from MDS to AML. Overall survival (OS) was determined from the date of diagnosis to the date of death or last follow-up visit.
Results
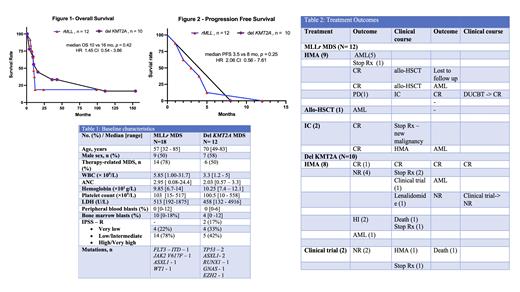
Between January 2005 to February 2021, 3369 patients (pts) with the diagnosis of MDS (n=2761) and CMML (n=608) were identified. Of these, 30 pts had MLL aberrations with 18 pts with MLL rearrangements (MLL r) and 12 pts with deletion 11q23 (del-KMT2A). Baseline characteristics are present in Table 1.
Among 18 pts with MLL r MDS, 6 pts did not undergo any therapy at our institution. Of the remaining 12, 9 (75%) pts received HMA based therapy, 1 (8%) patient (pt) proceeded to allogeneic stem cell transplant(allo-HSCT) and 2 (17%) pts received intensive chemotherapy (idarubicin, fludarabine and cytarabine). Of the 9 pts who received HMA therapy, 5 (56%) pts had transformation to AML, 2 (22%) pts achieved CR and underwent allo-HSCT, 1 (11%) pt had persistent disease and 1 (11%) developed concurrent metastatic sarcoma and stopped treatment. Out of the 2 (22%) pts who underwent allo-HSCT, 1 pt received maintenance HMA post-transplant but relapsed with transformation to AML after 9 months, and the other was lost to follow up. 1 (11%) pt who had persistent disease received intensive chemotherapy and went into CR and subsequently underwent double umbilical cord transplant and continues to remain in CR. The 2 (17%) pts who received intensive chemotherapy frontline both went into CR, but one developed concurrent malignancy and stopped treatment. The other pt was transitioned to HMA therapy but relapsed with transformation to AML. The 1 patient who received frontline allo-HSCT relapsed with transformation to AML after 5 months. The overall median follow-up duration was 24 months with a median OS of 10 months (Figure 1) and a median PFS of 3.5 months(Figure 2).
12 pts with del-KMT2A were identified, out of which 2 pts did not receive treatment. Of the remaining 10 pts, 8 (80%) received HMA based therapy and 2 (20%) pts received investigational treatments. Of the 8 pts who received HMA therapy, 1 (12.5%) achieved CR and remains in CR, 4 (50%) pts had no response, 2 (25%) had hematological improvement (HI) but one died of other causes and the other elected to stop treatment, 1 (12.5%) pt had transformation to AML. Of the 4 pts with no response, 2 pts elected to stop treatment, with 1 developing concurrent malignancy. Of the remaining 2 pts, 1 pt was placed on an investigational agent and had progression to AML and the other was placed on lenalidomide and then an investigational agent, but ultimately pursued hospice. Of the 2 pts on investigational agents both had persistent disease and one patient died and the other elected to stop treatment due to concurrent illness. The overall median follow-up duration was 154 months with a median OS of 16 months (Figure 1) and median PFS of 8 months (Figure 2). Clinical course is presented in Table 2.
Conclusion
Prognosis of patients with MLL alterations and MDS is very poor. MLL r MDS had worse outcomes with rapid transformation to AML compared to del-KMT2A. New therapies are needed for this group of patients.
Issa: Syndax Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kura Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding. Sasaki: Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jabbour: Amgen, AbbVie, Spectrum, BMS, Takeda, Pfizer, Adaptive, Genentech: Research Funding. Kantarjian: Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Aptitude Health: Honoraria; Ascentage: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz: Research Funding; Astellas Health: Honoraria; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria; Ipsen Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; KAHR Medical Ltd: Honoraria; NOVA Research: Honoraria; Precision Biosciences: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Taiho Pharmaceutical Canada: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal